Phaser objets¶
Géométrie¶
Ligne¶
// Création d'un « Graphics Game Object »
let graphics = this.add.graphics();
// @param lineWidth — The stroke width.
// @param color — The stroke color.
// @param alpha — The stroke alpha. Default 1.
graphics.lineStyle(3, 0xffffff, 1);
// Ligne horizontale
graphics.moveTo(200, 200);
graphics.lineTo(600, 200);
// Ligne verticale
graphics.moveTo(400, 100);
graphics.lineTo(400, 300);
graphics.strokePath(); // Important
Triangle¶
let graphics = this.add.graphics();
graphics.lineStyle(3, 0x406c55);
graphics.fillStyle(0x2fb170);
graphics.beginPath();
graphics.moveTo(400, 100); // Sommet
graphics.lineTo(500, 300); // Droite
graphics.lineTo(300, 300); // Gauche
graphics.closePath();
graphics.fillPath();
graphics.strokePath();
Carré¶
let graphics = this.add.graphics();
graphics.lineStyle(3, 0x5c5688);
graphics.fillStyle(0x9383e2);
let squareSize = config.height / 2;
let squareX = (config.width - squareSize) / 2;
let squareY = (config.height - squareSize) / 2;
// @param x — The x coordinate of the top-left of the rectangle.
// @param y — The y coordinate of the top-left of the rectangle.
// @param width — The width of the rectangle.
// @param height — The height of the rectangle.
graphics.fillRect(squareX, squareY, squareSize, squareSize);
// @param x — The x coordinate of the top-left of the rectangle.
// @param y — The y coordinate of the top-left of the rectangle.
// @param width — The width of the rectangle.
// @param height — The height of the rectangle.
graphics.strokeRect(squareX, squareY, squareSize, squareSize);
Polygone¶
let graphics = this.add.graphics();
graphics.lineStyle(3, 0x844a62, 1);
graphics.fillStyle(0xf06090, 1);
let sides = 6;
let polygonRadius = config.height / 3;
let centerX = config.width / 2;
let centerY = config.height / 2;
graphics.beginPath();
for (let i = 0; i < sides; i++) {
let angle = Phaser.Math.DegToRad((360 / sides) * i - 90);
let x = centerX + polygonRadius * Math.cos(angle);
let y = centerY + polygonRadius * Math.sin(angle);
if (i === 0) {
graphics.moveTo(x, y);
} else {
graphics.lineTo(x, y);
}
}
graphics.closePath();
graphics.fillPath();
graphics.strokePath();
Cercle / Ellipse¶
let graphics = this.add.graphics();
graphics.lineStyle(3, 0x344f95);
graphics.fillStyle(0x2977ff, 1);
// @param x — The x coordinate of the center of the circle.
// @param y — The y coordinate of the center of the circle.
// @param radius — The radius of the circle.
graphics.fillCircle(400, 200, 100);
// @param x — The x coordinate of the center of the circle.
// @param y — The y coordinate of the center of the circle.
// @param radius — The radius of the circle.
graphics.strokeCircle(400, 200, 100);
let graphics = this.add.graphics();
graphics.fillStyle(0x2977ff, 1);
graphics.lineStyle(3, 0x344f95, 1);
// @param x — The x coordinate of the center of the ellipse.
// @param y — The y coordinate of the center of the ellipse.
// @param width — The width of the ellipse.
// @param height — The height of the ellipse.
// @param smoothness — The number of points to draw the ellipse with. Default 32.
graphics.strokeEllipse(400, 200, 300, 200);
// @param x — The x coordinate of the center of the ellipse.
// @param y — The y coordinate of the center of the ellipse.
// @param width — The width of the ellipse.
// @param height — The height of the ellipse.
// @param smoothness — The number of points to draw the ellipse with. Default 32.
graphics.fillEllipse(400, 200, 300, 200);
Courbes¶
Bézier quadratique¶
let graphics = this.add.graphics();
graphics.lineStyle(2, 0xe6695b);
let startPoint = new Phaser.Math.Vector2(300, 200);
let controlPoint = new Phaser.Math.Vector2(400, 100);
let endPoint = new Phaser.Math.Vector2(500, 200);
// @param p0 — Start point, or an array of point pairs.
// @param p1 — Control Point 1.
// @param p2 — End Point.
let curve = new Phaser.Curves.QuadraticBezier(
startPoint,
controlPoint,
endPoint
);
curve.draw(graphics);
Pourquoi il faut faire .draw() ?
Les courbes peuvent servir à différentes choses en Phaser. Entre autres, elles peuvent servir de trajectoire pour une animation. Les courbes ne sont donc pas toujours destinées à être dessinées. Il faut le spécifier manuellement si c'est ce qu'on veut.
Bézier cubique¶
let graphics = this.add.graphics();
graphics.lineStyle(2, 0xe6695b, 1);
let startPoint = new Phaser.Math.Vector2(200, 200);
let controlPoint1 = new Phaser.Math.Vector2(200, 100);
let controlPoint2 = new Phaser.Math.Vector2(600, 300);
let endPoint = new Phaser.Math.Vector2(600, 200);
// @param p0 — Start point, or an array of point pairs.
// @param p1 — Control Point 1.
// @param p2 — Control Point 2.
// @param p3 — End Point.
let curve = new Phaser.Curves.CubicBezier(
startPoint,
controlPoint1,
controlPoint2,
endPoint
);
curve.draw(graphics);
Spline¶
let graphics = this.add.graphics();
graphics.lineStyle(2, 0xe6695b, 1);
// Create a smooth 2d spline curve from a series of points.
// @param points — The points that configure the curve.
let spline = new Phaser.Curves.Spline([
new Phaser.Math.Vector2(200, 200),
new Phaser.Math.Vector2(400, 100),
new Phaser.Math.Vector2(600, 200)
]);
spline.draw(graphics);
Arc¶
let graphics = this.add.graphics();
graphics.lineStyle(2, 0xe6695b, 1);
let startAngle = Phaser.Math.DegToRad(90);
let endAngle = Phaser.Math.DegToRad(0);
graphics.beginPath();
// @param x — The x coordinate of the center of the circle.
// @param y — The y coordinate of the center of the circle.
// @param radius — The radius of the circle.
// @param startAngle — The starting angle, in radians.
// @param endAngle — The ending angle, in radians.
// @param anticlockwise — Whether the drawing should be anticlockwise or clockwise. Default false.
// @param overshoot — This value allows you to increase the segment iterations in WebGL rendering. Useful if the arc has a thick stroke and needs to overshoot to join-up cleanly. Use small numbers such as 0.01 to start with and increase as needed. Default 0.
graphics.arc(400, 200, 100, startAngle, endAngle);
graphics.strokePath();
Combinaison¶
Texte¶
Simple¶
// @param x — The horizontal position of this Game Object in the world.
// @param y — The vertical position of this Game Object in the world.
// @param text — The text this Text object will display.
// @param style — The Text style configuration object.
const text = this.add.text(100, 100, "C’est ça l’été");
Stylisé¶
const styledText = this.add.text(50, 90, "C’est ça l’été !?", {
fontFamily: '"Arial"',
fontSize: "32px",
color: "#ff00ff",
backgroundColor: "#000000",
padding: {
x: 10,
y: 5
}
});
Google Fonts¶
<link rel="preconnect" href="https://fonts.googleapis.com">
<link rel="preconnect" href="https://fonts.gstatic.com" crossorigin>
<link href="https://fonts.googleapis.com/css2?family=DM+Serif+Text:ital@0;1&display=swap" rel="stylesheet">
const styledText2 = this.add.text(50, 150, "C’est ça l’été !?", {
fontFamily: '"DM Serif Text"',
fontSize: "26px",
padding: {
y: 5
}
});
Image¶
preload() {
this.load.image("img", "assets/images/fleche.png");
}
create() {
this.add.image(400, 100, "img");
}
z-index¶
Il est possible de gérer la profondeur du calque d'une image (z-index).
create() {
let img = this.add.image(400, 100, "img");
// @param value — The depth of this Game Object. Ensure this value is only ever a number data-type.
img.setDepth(1);
}
Tilemap¶
Transformations¶
Rotation¶
// Angle 0 - 360
this.add.image(40, 30, 'img').setAngle(30);
// Radiant 0 - 6.28318530718 (2*PI)
this.add.image(40, 30, 'img').rotation(4);
Réflexion¶
this.add.image(40, 30, 'img').setFlipX(true);
this.add.image(40, 30, 'img').setFlipY(true);
Origine¶
this.add.image(40, 30, 'img').setOrigin(0.5, 0.5);
Position¶
image.setPosition(400, 200);
image.x = 400;
image.y = 200;
Échelle¶
this.add.image(40, 30, 'img').setScale(2);
Alpha¶
this.add.image(40, 30, 'img').setAlpha(0.5);
Pistes sonores  ¶
¶
preload() {
this.load.audio('bg', 'assets/audio/ambient.mp3');
}
create() {
const music = this.sound.add('bg');
music.play({
loop: true,
volume: 0.5
});
}
Exercices¶
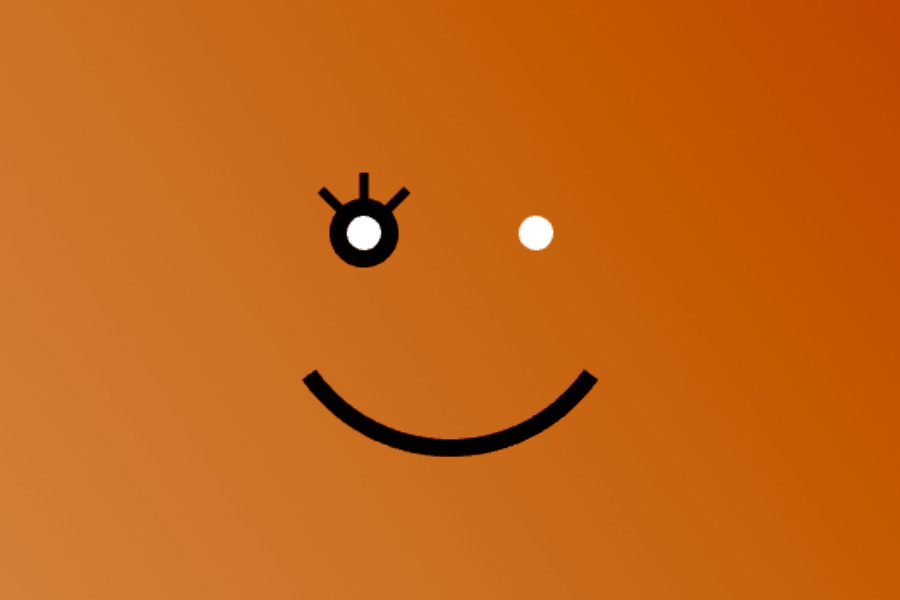

Exercice - Phaser
Orange mécanique
Exercice - Phaser
Damier
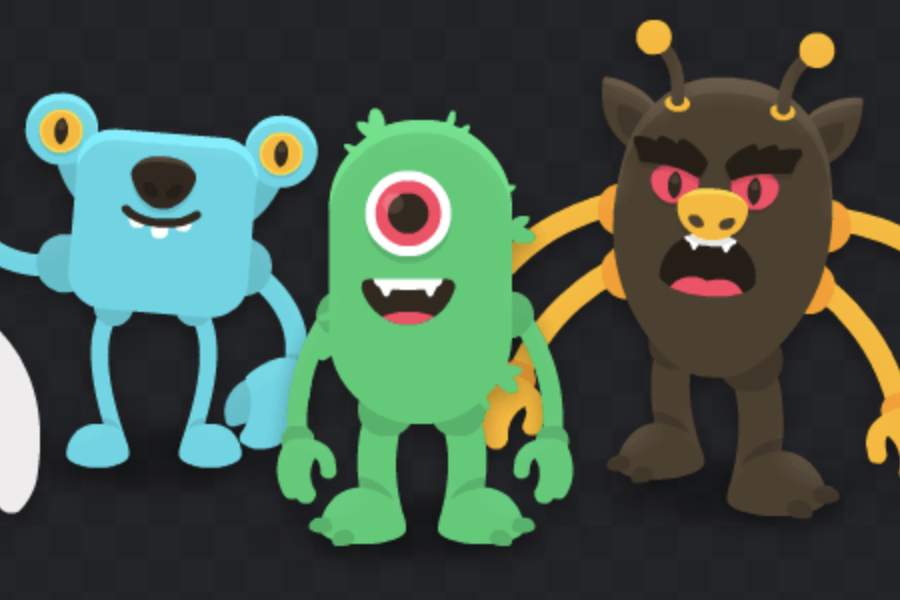

Exercice - Phaser
Monstruosité